Some 2,00,000 years ago, humans separated from other apes and developed a larger brain. Right from the beginning, we were explorers. Our ancestors traveled from continent to continent, crossing oceans thousands of miles across. We still have that exploring nature.
In the ancient times, humans used constellations and position of the stars in the night as a map. Stars change their position over millions of years. For our brief moment on the planet earth, they acted as a perfect stationary reference point.
However, star based navigation system had its own drawbacks. Firstly, this system is not useful in the daylight as light from the sun makes other stars invisible. Secondly, during a bad weather situation, clouds overshadow stars and create trouble for navigators.
Thanks to the modern technology, we do not have to rely on stars any more. Now we have satellites orbiting planet earth at the height of around 30,000 KM. These artificial satellites beam signals down to earth. Our smart devices catch these signals and tell us where we actually are on the planet.
Recently, it was all over the news that India has developed its own satellite navigation system. PM Modi has named the technology as NAVIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation). Many of fellow Indians are now curious about prospects and benefits of this new achievement.
► How Satellite Navigation Works?
Satellite navigation is a pretty advanced method of calculating a device’s location and it is really fun to learn how it works.
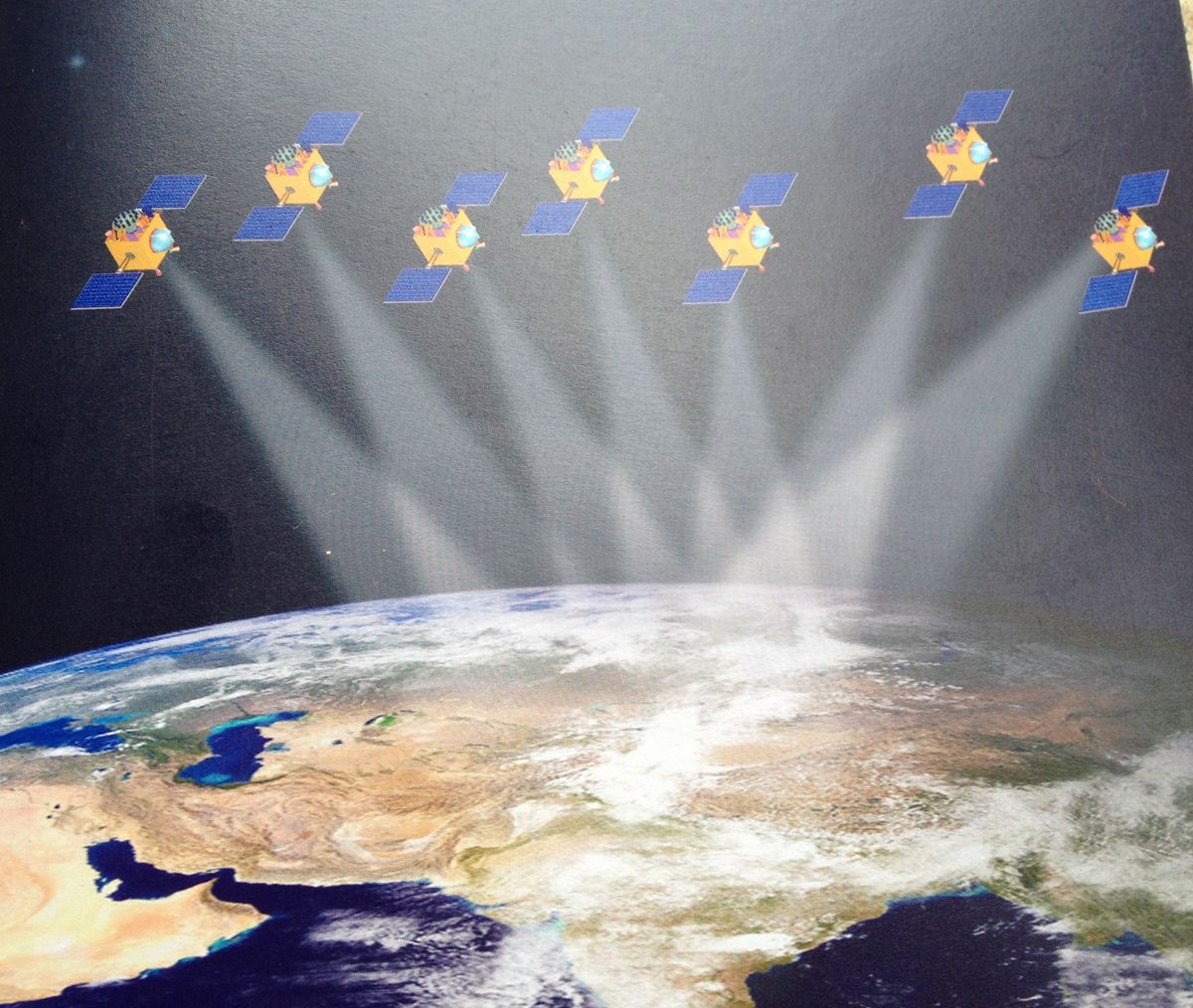
Scientists (and engineers) first launch a bunch of satellites in the orbit around the earth. Each of the navigation satellites broadcasts a signal back to earth continuously (24X7). These satellites generally operate on solar power. This signal contains the information about where the mother satellite (which sent the signal) is located in the orbit as well as the time when the signal was released from that satellite. The whole navigation system depends on the accuracy of time measurement, which is why all navigation satellites have atomic clocks on board.
Each satellite has its own circular coverage area. One thing to note here is the coverage area of different satellites overlaps. To get the location, a client device (a smartphone for instance) needs to receive broadcasted signal from at least three satellites. The client device calculates the time taken by the signal from each connected satellite to reach it. After applying a real differentiation and triangulation, the client device can show you the location.
If your navigation device is lucky enough to receive the signal from a fourth satellite then it will also tell the height of the platform on which you are standing.
The accuracy of the location depends on the radius of coverage area of each satellite of a navigation system, number of satellites a client device is connected and the level of technology.
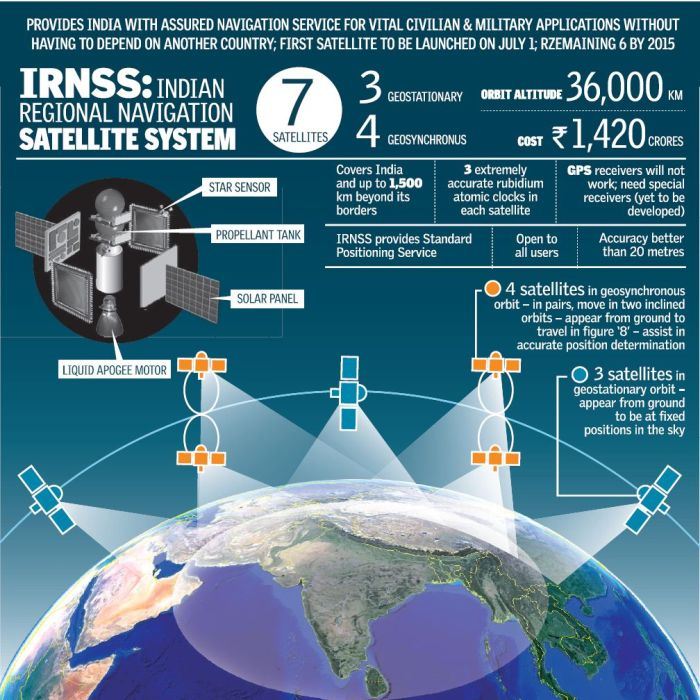
► NAVIC Explained!
The IRNSS or NAVIC is based on a system of seven satellites orbiting the planet earth. ISRO has also planned to keep two additional satellites in standby mode on earth in case any orbiting satellite fails.
Our indigenous navigation system has a coverage area of about 1500 KM. It not only covers Indian subcontinent but also the surrounding areas like Eastern Africa, Western Australia, Pakistan, Bangladesh, China, Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, Singapore and also the Northern Indian Ocean.
ISRO launched the first satellite of the NAVIC system in 2013 and the seventh on 28 April 2016. The project is currently in testing phase. Scientists expect it to become fully operational around June, this year (2016). The task that ISRO will now focus on is of creating front-end chips for receiving and interpreting the satellite signals.
► NAVIC vs. GPS & Other Navigation Technologies
Well, NAVIC is not the only satellite navigation system in the world. The most famous navigation system that every smartphone in the world uses is United States’ GPS or Global Positioning System. GPS currently has 31 satellites in orbit and offers a global coverage with the accuracy of up to 5 meters to general citizens.
GLONASS is Russia’s alternative to GPS, which also offers world coverage. The precision of GLONASS navigation system varies between 5-10 meters.
European Union’s Galileo and China’s next-gen BeiDou are also under development. Both these systems plan to cover the globe.
In comparison to all these navigation systems, NAVIC is lagging a little behind. It broadcasts signals to only a limited region and gives an accuracy of up to 10 meter or less on the Indian subcontinent and of about 20 meters in the surrounding region. I would also like to point out though there is nothing to worry about. There are only five countries in the world with their own satellite navigation system and Bharat has become one of them.
We are behind satellite navigation systems of other countries just because our politicians do not take interests in science and technology. I just hope that this situation changes in the coming days.
► NAVIC Benefit to an Average Citizen
Okay, so we have our own satellite navigation system in place now. How will it benefit common people?
To be honest, NAVIC is not going to directly benefit the general public, not unless other navigation systems become hostile. United States’ GPS is already offering accuracy of up to 5 meters, which is greater than that of NAVIC’s.
One thing to point out here is NAVIC can help in locating your client device faster by working together with GPS. For that though, manufacturers will have to implement NAVIC front-end chips on smartphones and other dedicated navigation devices.
Smartphone manufacturers are already struggling with limited space on mobile phones. Considering this scenario, it is a little unlikely that any multi-national brand will pay attention to NAVIC. I am not saying it cannot happen. The Government of India can certainly make a difference by offering some kind of incentives to manufacturers who will offer NAVIC on their devices.
► NAVIC as a Status Symbol
The world has always underestimated India’s ability but we have continuously proved them wrong. Certainly, we are proud of ISRO. First, our space agency launched Chandrayan, then Mangalyan and now we have an indigenous satellite navigation system.
This clearly shows how capable India as a country is. ISRO has done all this even when it does not get a lot of money from the government. The space agency has only spent 280 crore rupees for placing each NAVIC satellite in the orbit, which is significantly less than what other developed countries spend on their satellites. In fact, NASA’s yearly budget is ten times the budget of ISRO.
The whole world was surprised when ISRO successfully completed the Mangalyan mission for under 500 crores rupees and that also in just one go.
NAVIC is a new gem in India’s crown. Parents should tell their children about this achievement as it will inspire them to become the scientists of future.
► Indigenous Navigation System – Independent Military
Now that India has an indigenous satellite navigation system, we do not have to depend on other countries.
Although GPS is freely available to every person in the world but no one can predict how a future war situation will turn out to be. What happened during Kargil War is a clear example of what I am trying to portray.
Many countries are developing or are planning to develop their own navigation system to become self-dependent on the front of satellite navigation. Indian has done this already.
Manipulating GPS or GLONASS according to regional needs is not possible because these systems are owned by other countries.
Now, our military can perform any type of action without telling the US or Russia about it. We can use NAVIC any way we want.
Generally, navigation systems offer two services i.e. location services for general public and location services for military. The GPS and GLONASS services reserved for military are more accurate but US and Russia do not offer these to armed forces of other countries. With NAVIC, Indian military will now have an accuracy that was not available to it before.
This achievement will also help our scientists in doing various researches. The NAVIC system can help in tracking traffic, doing other kind of scientific surveys and for monitoring forest life.
► Extending the Help to Other Countries
India always tries to help other countries. It is obvious that our government will allow the neighboring countries to use NAVIC once it becomes available. In fact, after the launch of the seventh satellite of the NAVIC system, PM Modi even welcomed countries of the South Asia to take benefit from our indigenous satellite navigation system.
Considering this, NAVIC will help India in strengthening its relationship with neighboring countries.
Future Development of NAVIC: As of now, ISRO has not published any plans regarding the future development of NAVIC. After the testing phase, the first thing the space research body will do is developing two standby satellites that would be launched in case of any fault in the existing satellites. In my opinion, India will now wait for a decade to see how NAVIC turns out before adding new satellites to the system.